Institutional Distinctiveness (2023-2024)
Developmental Plan of DMIHER (DU) aligned with UNs Sustainable Development Goals
Background
Transforming our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development
The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, adopted by all United Nations Member States in 2015, provides a shared blueprint for peace and prosperity for people and the planet. At its core are the 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), which are an urgent call for action by all countries - developed and developing - in a global partnership. It intends to take the bold and transformative steps which are urgently needed to shift the world onto a sustainable and resilient path. The 17 Sustainable Development Goals and 169 targets demonstrate the scale and ambition of the universal Agenda of eradicating poverty, realizing the human rights and achieving gender equality and empowerment of all women and girls and thus heal and secure our planet. At the core of this global agenda for 2030 is the principle of universality: ‘Leave No One Behind’. This comprehensive agenda recognises that it is no longer sufficient just to focus on economic growth, but on fairer and more equal societies, and a safer and more prosperous planet. The 17 SDGs are integrated, indivisible and balance the three dimensions of sustainable development: the Economic, Social and Environmental.
The historical trajectory of this declaration is as depicted in fig 1 :
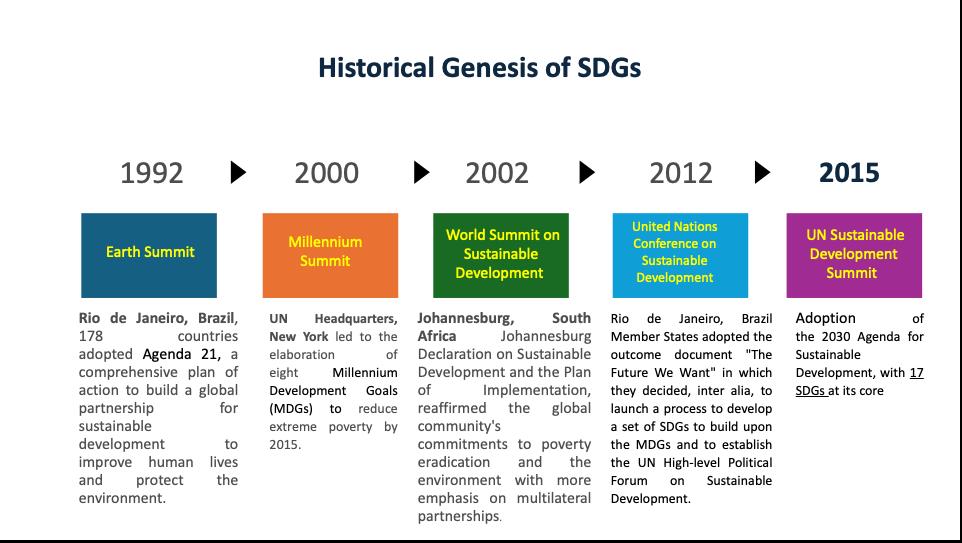
Fig 1 : Historical genesis of UNs Sustainable Developmental Goals
The UNs General Assembly Economic and Social Council in its 2024 global report regarding ‘Progress towards the Sustainable Development Goals’ reveals that only seventeen percent of SDGs targets are on track to be achieved, nearly half are showing minimal or moderate progress and progress on over a third has stalled or even regressed. The COVID-19 pandemic, a growing number of conflicts, geopolitical and trade tensions and the ever-worsening effects of climate change have combined to leave the progress on SDGs on a slow pace. Good progress has been made on issues such as reducing the global infant mortality rate, the incidence of HIV infections and the cost of remittances, and on increasing access to water and sanitation, energy and mobile broadband. In addition, many countries are pursuing SDG transformation with real determination and they are making tangible progress.
DMIHER’s development plan aligned to the global development Agenda 2030 :
- Vision 2035 : Higher education institutions (HEIs) have a very high potential, as their research, innovation, engagement and development of human capital are essential steppingstones for the contribution of the SDGs. With a deadline of 2030, the urgency of the situation demands that all Education sectors galvanize to secure greater participation and leadership, more resources and better solutions to address the 2030 agenda. DMIHER, in its timely attempt to align its Institutional developmental Plan 2035 to global developmental agenda , has incorporated eight developmental indicators for SDGs along with year-wise targets for all constituent units of the University. The 8 developmental indicators are as follows ;
- Number of senior female academic/administrative faculty
- Scientific events on SDGs in collaboration with GOV & Non-Gov agencies
- International Consortia projects (Partnership for SDGs)
- Collaborations with health institutions
- Shared sports facilities
- Proportion of first-generation students
- Vocational training events (Host events at university that are open to the general public)
- Student Diversity (Students from Other State/Other Country)
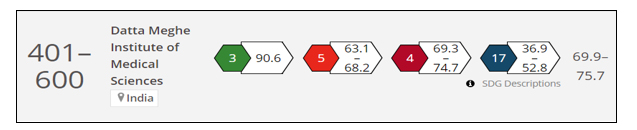
- Accreditations and Rankings in SDG : In order to validate its quest towards realization of Global agenda on sustainability, understand the trends and practices and consistently make efforts for reducing inequalities and towards a greener future, the University has participated in TIMES Impact Rankings consistently. The Global standing of the University is such rankings is as depicted below :
- The National Education Policy 2020 : National Education Policy 2030 in its Global education development agenda seeks to ensure inclusive and equitable quality education and promote lifelong learning opportunities for all by 2030.
- NAAC : The revised National accreditation framework identifies International benchmarks as revised framework for all HEIs through Binary and Maturity based graded accreditation. The SDG indicators are few of the key parameters in the revised framework.
- NIRF : The recent revision in National NIRF rankings include SDG parameters and have initiated rankings in SDG category as well.
- Teaching: All academic programs incorporate elements of education for the SDGs into formal and informal learning and teaching activities in universities. There are various initiatives that provide students with the necessary skills to implement the SDGs, such as strategic vision, design-thinking, social responsibility, problem-solving, anticipatory skills and interdisciplinary collaboration.
- Gender Equality: Proactive policies are in place to ensure gender equality. Women in top leadership roles, Institutional forum for women, Gender champions, Internal complaint committee for prevention of sexual harassment of women at workplace, grievance redressal mechanisms, transgender policy are few such initiatives to ensure gender equality. Every constituent unit can engages with local communities and contribute to society's progress towards gender equality.
- Community engagement: DMIHER is committed to bridging the gaps between the community and health services, addressing inequity in access to reducing inequalities in health care, and improving health-seeking behavior. DMIHER launched the ‘AROGYA-SETU’ program in 2005, aimed at providing holistic healthcare to the community, Community-based education, health insurance services & undertaking evidence-based scientific research. AROGYA-SETU was recognized as a Center of Excellence in 2017. Holistic healthcare services to communities of reach by bridging the community and healthcare facilities, including access to tertiary healthcare. There are Community insurance programs to make health care financially accessible and improve utilization public insurance programs like Ayushman Bharat and MJPGY. Community services are linked to academic programs at DMIHER which creating opportunities for students to practice what they learn, adopt families in villages, undertake awareness programs, rural/tribal research, and inculcate the core values of empathy and compassion.
- Academic and Operational Infrastructure & services: The University focusses on Sustainable infrastructure, Solar energy conservation , rainwater harvesting, Green campus, reduced carbon emission by use of e rickshaw, e bikes with charging stations, use of public transportation, carpooling and sustainable waste management by reducing waste and composting. Campus Perspective developmental Plan for 5 years incorporates all principles of energy conservation, recycling and green initiatives. Green , energy and Environmental audit are done every year and the suggestions are acted upon in a timely manner.
- Management practices: DMIHER’s annual calendar integrates SDGs aligned collaborative activities through National and International partnerships with eminent organisations, Government and NGOs. It also integrates SDG principles in overall University Governance and culture.
- Annual SDG report : The University publishes annual report on various SDG aligned initiatives of the University on its website and submits the same to SDG accord.
- DMIHER signatory to SDG accord : DMIHER is signatory to global SDG Accord which recognises the critical role that education has in delivering the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). The Accord is a commitment made to take initiative for SDGs, annually report on progress as a Signatory, and do so in ways which share the learning with partner institutions both nationally and internationally. A total of 408 Universities and colleges across the globe are signatory to this SDG accord till date.

- Innovation Ecosystem : The DMIHER Institutional innovation Council systematically fosters a culture of innovation amongst the learners and faculty through a thriving entrepreneurship ecosystem in the University. Workshops on IPR, design thinking and Innovation, Entrepreneurship, and developing start-ups are organized regularly in addition to Hackathons, idea competitions etc. in coordination with Biomedical Engineering and Technology Innovation Centre (BETIC) innovation cell. The New Gen Innovation Entrepreneurship Development Centre (NEWGEN IEDC) channelizes learners to become active partners in developing knowledge-based and innovation-driven enterprises Various high-end facilities, centers, platforms, and grant opportunities, including seed fund support, co-working space, Advanced computing facilities, Fabrication Laboratory, mentorship for innovators and startups, have been created to ignite innovation and entrepreneurship culture. DMIHER encourages ideas to promote Higher-Order Cognitive capacities among students/ researchers and kindle curiosity among them as a basis for Research. Systematically foster the culture of nurturing ideas for enabling innovation and a thriving entrepreneurship
SDG |
2022 Rankings |
2024 Rankings |
3 |
47th |
15th |
4 |
401-600 |
101-200 |
5 |
top 200 |
101-200 |
9 |
|
601-800 |
17 |
601-800 |
1001-1500 |
Overall |
401-600 |
401-600 |
As such , Government is united in its commitment towards achieving SDG goals through NITI AYOG. NITI Aayog, works closely with States and UTs to oversee the adoption and monitoring of the SDGs in the country and promote competitive and cooperative federalism among States and UTs. Various National Accreditations and Rankings have SDG parameters and accordingly DMIHER has aligned its operations and SOPs in realising the 17 goals:
DMIHER was recently was awarded with ‘Institutional Social responsibility’ award for its cognizable work in community and society by FICCI.
References :
- https://sdgs.un.org/goals
- https://unstats.un.org/sdgs/files/report/2024/SG-SDG-Progress-Report-2024-advanced-unedited-version.pdf
- https://www.niti.gov.in/overview-sustainable-development-goals
- https://www.education.gov.in/sites/upload_files/mhrd/files/NEP_Final_English_0.pdf
- https://www.education.gov.in/sites/upload_files/mhrd/files/REPORT-1.pdf
- https://www.educationtimes.com/article/campus-beat-college-life/99736372/nirf-2025-to-introduce-sustainability-in-rankings-to-increase-green-campuses
- https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2023/09/why-universities-are-so-important-for-hitting-the-sdgs-by-2030/
